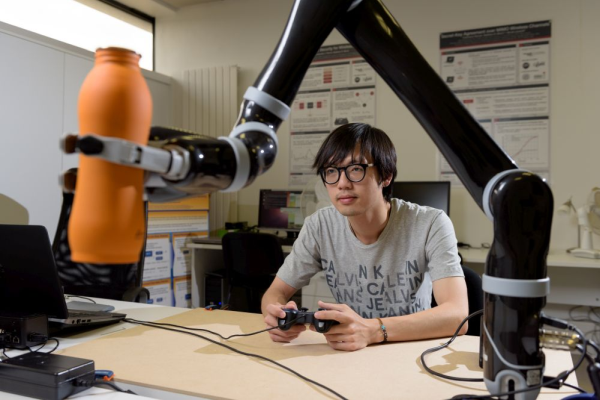
Foundations of Robotics
Research in the foundational concepts of robotics and automation covers an interdisciplinary range of topics. Computational methodologies, electronics engineering, and physics are all foundational areas of robotics research. Sub-topics include simulation, kinematics, control, optimization, and probabilistic inference.
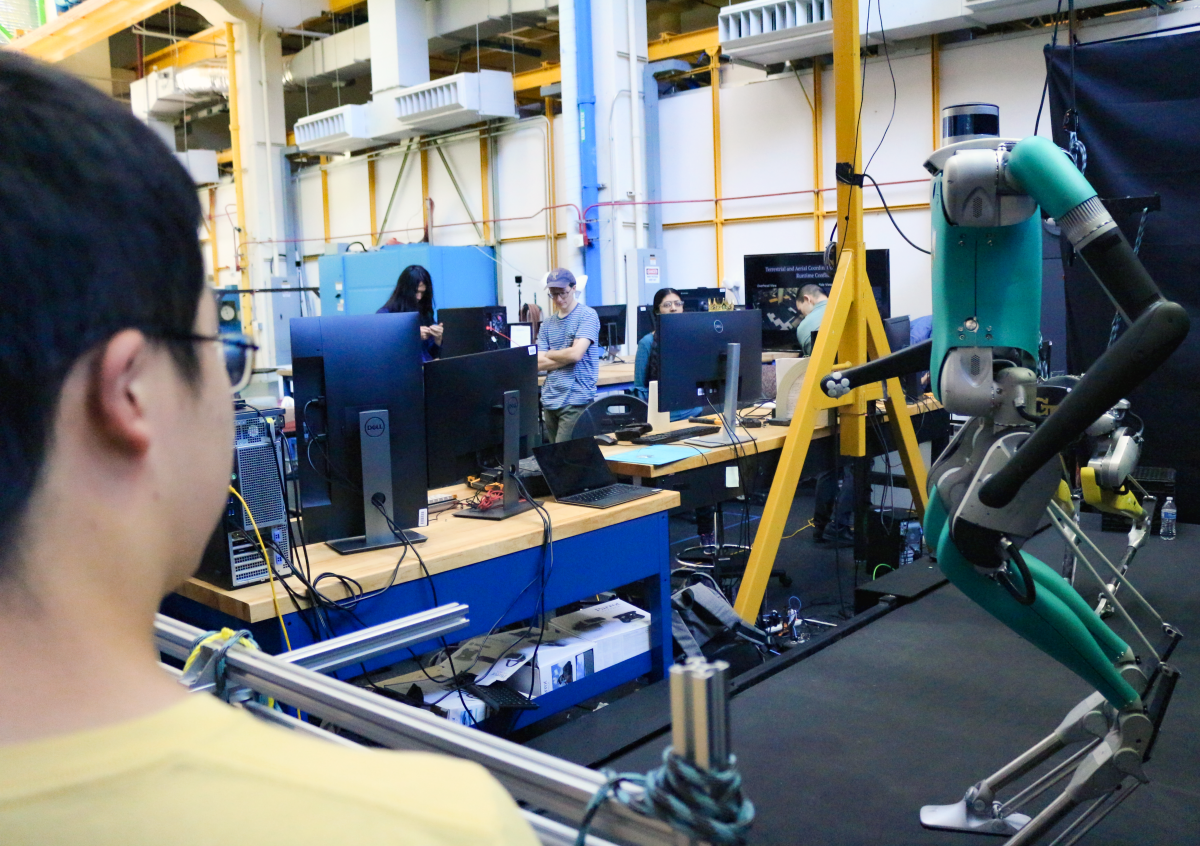

Field & Service Robotics
Field robots are mobile robots that operate in dynamic environments. These robots are adaptive, and responsive working in variable conditions and territories. Service Robots are fully or partially autonomous and perform tasks that are dangerous, repetitive, or hazardous. This research area also comprises simple and complex industrial robots as well as frontline service robots.
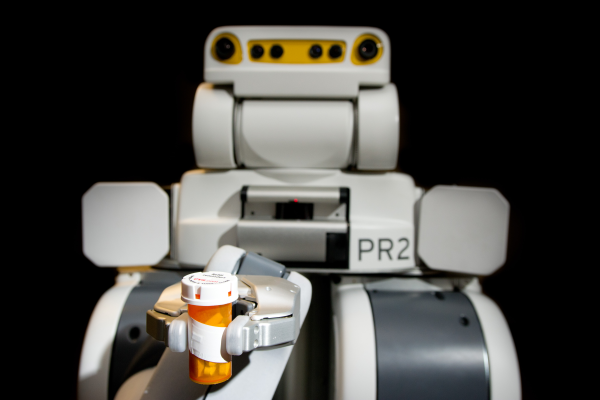

Human-Centered Robotics
Human-centered robotics focuses on robots that interact, assist and cooperate with humans requiring robot operation in human environments and close interaction with non-professional users. The research spans broad areas in human-robot interaction including; assistive and rehabilitation robotics, robotic systems design, wearable robotics, biomedical, surgical and clinical robots.

Manipulation & Locomotion
Robotic manipulation addresses the frameworks of modeling, motion planning, and control of grasp and manipulation of an object for a task. Manipulation research deals not only with the way in which the robot performs, but also the numerous operator-robot interface options. Once a task is defined, robots must be able to navigate its environment successfully. Legged, wheeled, articulated and winged are just a few of the way in robots are constructed for their specific tasks. Many of IRIM’s faculty are working to advance robotic locomotion, creating multi-environment capable robots and bespoke design options.

Safe, Secure, & Resilient Autonomy
Robots given a high degree of autonomy require formal assurances on their abilities and resiliency in the face of disruptions and uncertainty. Obtaining these assurances requires innovations across an interdisciplinary range of topics including control theory, machine learning, optimization, and formal methods for designing cyber-physical intelligent machines. By establishing a rigorous mathematical foundation of guaranteed performance, robots can be confidently deployed in safety-critical settings---for example, alongside humans---or for long durations without operator input such as underwater or in space.

Sensing & Perception
Robotic perception is related to many applications in robotics where sensory data and artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) techniques are involved. Examples include; object detection, environment representation, scene understanding, human/pedestrian detection, activity recognition, semantic place classification, and object modeling.