Gregory Sawicki
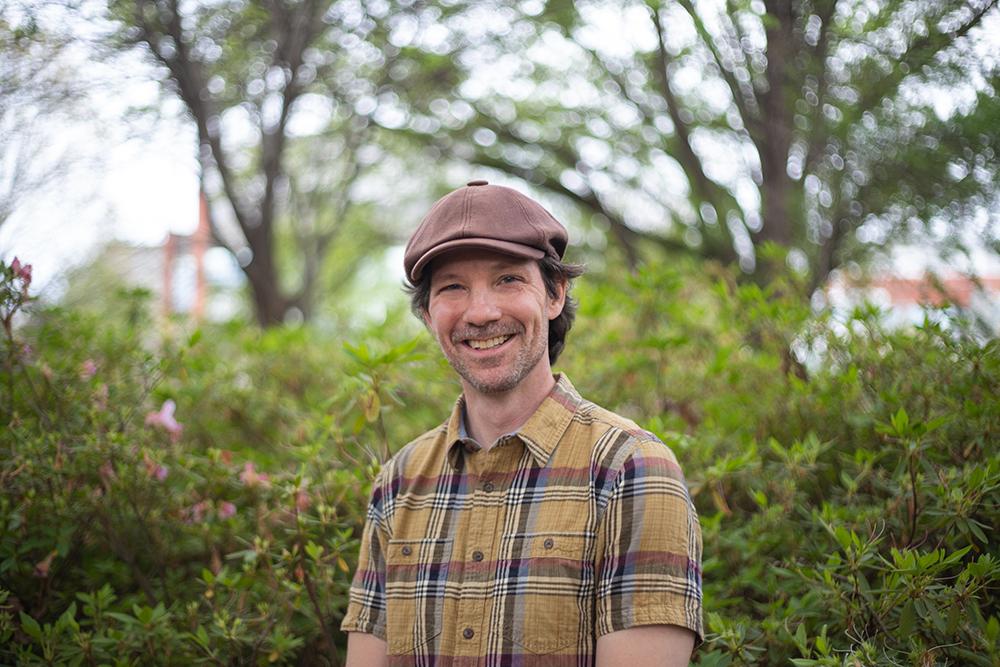

Dr. Gregory S. Sawicki is the Interim Executive Director of the Institute for Robotics and Intelligent Machines and Professor and Joseph Anderer Faculty Fellow at Georgia Tech with appointments in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering and the School of Biological Sciences. He holds a B.S. from Cornell University ('99) and a M.S. in Mechanical Engineering from University of California-Davis ('01). Dr. Sawicki completed his Ph.D. in Human Neuromechanics at the University of Michigan, Ann-Arbor ('07) and was an NIH-funded Post-Doctoral Fellow in Integrative Biology at Brown University ('07-'09). Dr. Sawicki was a faculty member in the Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering at NC State and UNC Chapel Hill from 2009-2017. In summer of 2017, he joined the faculty at Georgia Tech with appointments in Mechanical Engineering 3/4 and Biological Sciences 1/4.
wearable robotics; exoskeletons; locomotion; biomechanics; muscle mechanics